Understanding Gear Ratios and Their Impact on Vehicle Performance
Estimated reading time: 10 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Gear ratios determine how engine power converts into motion, affecting acceleration, torque, and fuel efficiency.
- The diff gear ratio calculator helps vehicle owners select the optimal gear ratio for their specific needs.
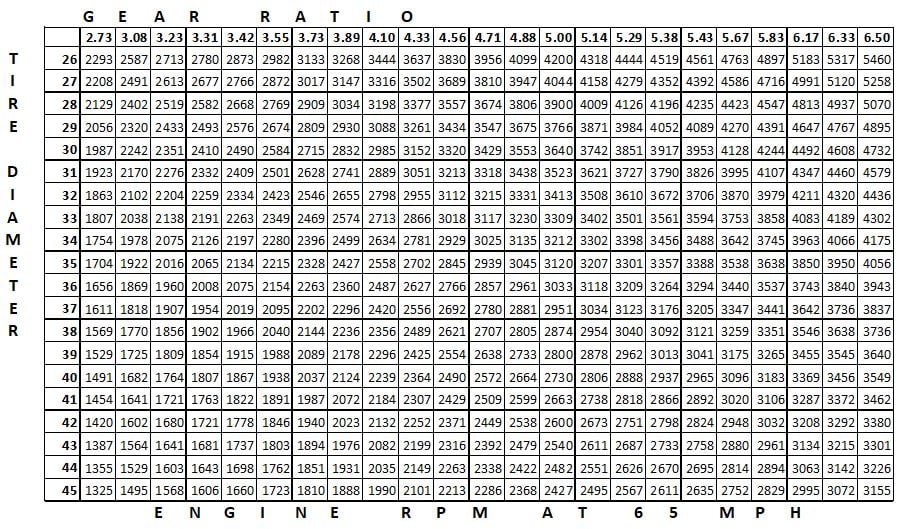
- Comparing 4.56 vs 4.88 gears illustrates the trade-offs between torque and fuel consumption.
- Upgrading to larger tires impacts the effective gear ratio; choosing the right gears compensates for performance changes.
- Proper installation and break-in procedures are crucial to prevent issues like gear whine after a swap.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Have you ever wondered how a vehicle efficiently transforms engine power into motion? The secret often lies in the gear ratio. A gear ratio is fundamentally the comparison between the rotation speeds of two or more interlocking gears. In simpler terms, for cars, it determines how many times the driveshaft spins to make the wheels turn once. For example, a gear ratio of 4.56 indicates that the driveshaft revolves 4.56 times for each complete wheel rotation. It’s a crucial factor that impacts vehicle performance aspects such as acceleration, torque, and fuel efficiency. Moreover, choosing the right gear ratio becomes essential when customizing vehicles for specific purposes—whether it be towing, racing, or off-roading. Tools like the diff gear ratio calculator play a vital role in assisting vehicle owners to select the optimal gear ratio, ensuring a balance between performance and fuel economy.
Understanding gear ratios is pivotal for maintaining a well-performing vehicle, as incorrect ratios can lead to poor acceleration and increased fuel consumption. Whether you’re upgrading your tires, the diff gear ratio calculator can simplify the selection by focusing on individual vehicle needs.
Learn more about how gear ratios work here: How Gear Ratios Work.
What is a Diff Gear Ratio Calculator?
Definition and Purpose
A differential (diff) gear ratio calculator is a handy tool that determines the optimal gear ratio for a vehicle’s differential. By inputting parameters like tire size, desired speed, and engine RPM, the calculator suggests the best gear ratio for achieving the desired performance outcomes, such as improved acceleration or fuel efficiency. This tool simplifies the complex calculations traditionally required to make informed decisions about gear setups. It takes much of the mechanical guesswork out of selecting gears for various modifications on your vehicle.
Check out how a gear ratio calculator works here: Gear Ratio Calculator.
How It Works
Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Diff Gear Ratio Calculator
- Gather Necessary Information
- Tire size (diameter or circumference)
- Current gear ratio
- Desired engine RPM at cruising speed
- Vehicle speed (usual cruising speed)
- Input Data into the Calculator
- Enter the above data into the corresponding fields of the calculator.
- Review the Results
- The calculator provides the optimal gear ratio, illustrating its impact on engine RPM and vehicle speed.
- Make Informed Decisions
- Use the results to guide your gear ratio choice.
- Adjust inputs to view different scenarios and their impact.
For instance, when upgrading to larger tires, entering the new tire size into the calculator will illustrate the effect on the overall setup. Using a diff gear ratio calculator ensures you have the precise data to make sound decisions regarding gear selection.
Understanding Gear Ratios: Comparing 4.56 vs 4.88 Gears Fuel Use
Explanation of Gear Ratios 4.56 vs 4.88
When considering gear ratios, common figures include 4.56 and 4.88, each serving unique uses:
- 4.56 Gear Ratio
- The driveshaft turns 4.56 times for one full wheel rotation.
- Balances torque, which is the twisting power transmitted to the wheels, and fuel efficiency.
- 4.88 Gear Ratio
- The driveshaft turns 4.88 times per wheel rotation.
- Delivers more torque, beneficial for heavy loads or steep terrains, but results in higher RPMs at cruising speeds.
For an in-depth explanation, visit: Rear-End Gear Ratio: What is it?.
Impact on Fuel Use
- 4.56 Gears Fuel Use
- Operates at lower engine RPM while cruising, enhancing fuel efficiency on highways.
- 4.88 Gears Fuel Use
- Results in higher RPMs at the same speed, increasing fuel consumption noticeably.
Situations to Prefer Each Gear Ratio
- 4.56 Gear Ratio
- Suitable for daily driving, moderate towing, and when fuel efficiency is a priority.
- Ideal for vehicles frequently on highways.
- 4.88 Gear Ratio
- Best for heavy towing, off-roading, or when using much larger tires.
- Prioritizes power and torque over fuel economy.
Real-World Examples
Consider a driver who upgrades to larger tires and notices decreased acceleration. Using a diff gear ratio calculator, they find moving from a 4.56 to a 4.88 ratio helps regain performance, even at a slight decrease in fuel efficiency.
Choosing Gears for Larger Tyres
When shifting to larger tires, the vehicle’s effective gear ratio changes. Larger tires increase the diameter, affecting the wheel’s rotation speed and lowering the engine RPM at given speeds, which may reduce the vehicle’s acceleration power. Therefore, choosing the right gear ratio compensates for these changes and maintains performance.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Gears
- Vehicle Weight
- Heavier vehicles may need lower gear ratios (higher numerical value) for enhanced acceleration.
- Intended Use
- Off-roading, towing, or racing requirements influence gear choice.
- Engine Characteristics
- The engine power band and torque curve should align with the gear ratio for optimized performance.
- Driving Conditions
- Consideration for frequent highway versus city driving impacts the balance between fuel efficiency and power.
Using a Diff Gear Ratio Calculator
By inputting the new larger tire size, the calculator shows the adjusted gear ratios one might need to return the vehicle to its factory performance levels. This ensures you meet performance expectations without sacrificing efficiency.
Visit here for more insights: Gear Ratio Calculator.
Tips for Balancing Performance and Fuel Efficiency
- Choose ratios that return engine RPM to the recommended range at cruising speeds.
- Avoid ratios that lead to needlessly high RPMs and increased wear.
Ring & Pinion Break-In Procedure
The ring and pinion are a differential’s central gears, crucial for transmitting engine power to the wheels. Their installation and break-in are paramount for ensuring longevity and performance.
Understanding the Ring and Pinion
- Ring Gear
- A larger gear attached to the differential carrier that meshes with the pinion gear.
- Pinion Gear
- A smaller gear that connects to the driveshaft, driving the ring gear.
Importance of Proper Break-In
Proper break-in ensures your gears last longer, perform better, and avoid issues like premature wear and noise.
Detailed Break-In Procedure
- Initial Installation Steps
- Correctly install with appropriate torque specifications, ensuring gear patterns are set correctly by checking backlash and contact patterns.
- Proper Lubrication Techniques
- Use gear oil recommended by the manufacturer, which may include specific additives, ensuring gears are fully lubricated before sealing the differential.
Read more about gear ratios here: Rear-End Gear Ratio: What is it?.
Breaking-In Period
- First 500 Miles
- Drive gently; avoid aggressive driving or towing, letting the gears cool after brief drives.
- Post 500 Miles
- Change the differential oil to eliminate wear particles and continue normal driving.
Maintenance Tips
- Regularly inspect for leaks or unusual noises.
- Adhere to fluid change intervals as prescribed.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Skipping the Break-In Process
- Can lead to gear failure and void warranties.
- Using Incorrect Oil
- May not offer sufficient protection, causing gear failure.
- Improper Installation
- Incorrect gear settings can cause issues like gear whine or failure.
Diagnosing Gear Whine After Swap
After swapping gears, gear whine can arise, usually signifying setup or component problems.
Understanding Gear Whine
This noise is a high-pitched sound heard during different driving conditions like acceleration or cruising, indicating gear installation or component issues.
Common Causes
- Improper Gear Setup
- Incorrect backlash or pinion depth settings.
- Worn or Damaged Components
- Bearings, gears, or shafts may be worn or incurred damage during installation.
- Inadequate Lubrication
- Incorrect or old gear oil leads to increased friction and noise.
Step-by-Step Diagnostic Process
- Identify When the Noise Occurs
- Determine if the whine happens during acceleration, deceleration, or at a constant speed.
- Inspect the Differential Fluid
- Check fluid levels and contamination signs like metal shavings.
- Examine Gear Installation Settings
- Recheck backlash and contact patterns and adjust pinion depth if necessary.
- Check Bearings and Components
- Look for wear or damage, ensuring bearings are properly seated.
- Test Drive After Adjustments
- Conduct a test drive to see if adjustments resolved the issue.
Solutions and Preventive Measures
- Correct Installation Errors
- Reset gear mesh and backlash as per manufacturer guidelines.
- Replace Worn Components
- Use new gears or bearings where necessary.
- Use Proper Lubrication
- Correctly fill gear oil types and amounts.
- Professional Assistance
- When needed, consult a mechanic or differential specialist.
Conclusion
Understanding gear ratios and selecting the correct one significantly impacts vehicle performance and efficiency. Using a diff gear ratio calculator makes tailoring your car easier, ensuring you hit the performance marks without increasing fuel consumption needlessly. Always ensure proper installation and follow a thorough break-in procedure for longevity and to avoid gear whine.
Final Tips
- Proper Installation and Break-In
- Follow guidelines to prevent potential problems.
- Regular Maintenance
- Schedule inspections and fluid changes.
- Consult Professionals
- Seek advice from experts when uncertain about modifications or issues.
Additional Resources
- Online Diff Gear Ratio Calculators and Tools
- Use this link for gear ratio computations: Gear Ratio Calculator.
- Technical Articles and Guides
- Gain deeper insight: Rear-End Gear Ratio: What is it?, Gear Ratio Explained with Charts, Formulas, and Resources.
For anyone considering gear changes or significant vehicle modifications, these resources and best practices will help you maintain a balance between performance and reliability.
